What is Rabies virus
Rabies virus is a rod- or bullet-shaped, single-stranded, negative-sense, unsegmented, enveloped RNA virus. The virus genome encodes five proteins. The rabies virus infects the central nervous system of mammals, ultimately causing disease in the brain and death.
What’s the structure of Rabies virus
The rabies virus is a negative-sense, non-segmented, single-stranded RNA virus measuring approximately 60 nm × 180 nm. It is composed of an internal protein core or nucleocapsid, containing the nucleic acid, and an outer envelope, a lipid-containing bilayer covered with transmembrane glycoprotein spikes.
The virus genome encodes five proteins associated with either the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex or the viral envelope (See figure below). The L (transcriptase), N (nucleoprotein), and NS (transcriptase-associated) proteins comprise the RNP complex, together with the viral RNA. These aggregate in the cytoplasm of virus-infected neurons and compose Negri bodies, the characteristic histopathologic finding of rabies virus infection. The M (matrix) and G (glycoprotein) proteins are associated with the lipid envelope. The G protein forms the protrusions that cover the outer surface of the virion envelope and is the only rabies virus protein known to induce virus-neutralizing antibody.
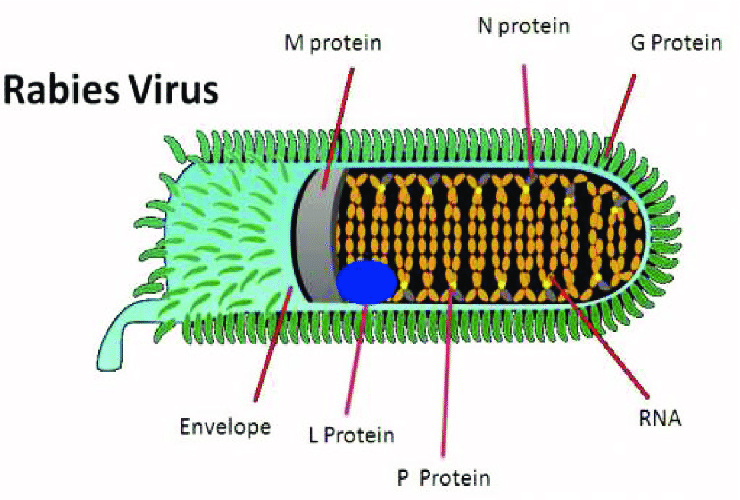
Figure 1.The structure of Rabies virus.
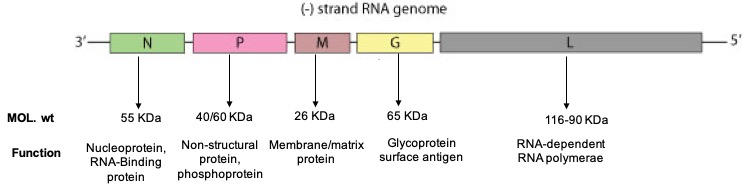
Figure 2.Rabies Virus Genome and encoded protein.
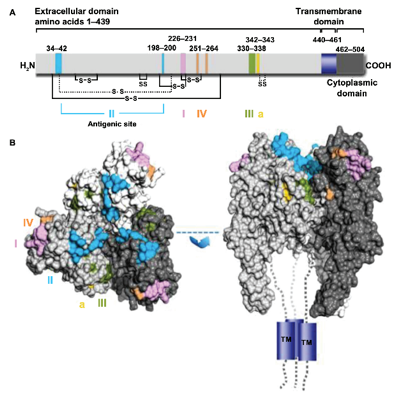
Figure 3.Representation of antigenic sites on the mature rabies virus glycoprotein G.
How does Rabies virus replicate
The replication of rabies virus is believed to be similar to that of other negative-stranded RNA viruses. The virus attaches to the host cell membranes via the G protein, penetrates the cytoplasm by fusion or pinocytosis, and is uncoated to RNP.
The core initiates primary transcription of the five complementary monocistronic messenger RNAs by using the virion-associated RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Each RNA is then translated into an individual viral protein. After viral proteins have been synthesized, replication of the genomic RNA continues with the synthesis of full length, positive-stranded RNA, which acts as a template for the production of progeny negative-stranded RNA.

Figure 4.A simplified rabies virus life cycle.
A simplified rabies virus life cycle in an infected cell can be divided into three different phases. The first phase includes binding and entry into the host cell by endocytosis (step 1), followed by fusion of the viral membrane and endosome membrane to release the viral genome (uncoating; step 2). In the second phase, virion components are produced (transcription, replication and protein synthesis; step 3). The last phase of the life cycle is the assembly of the viral components and budding and release of the rabies virus virions (step 4), which can start a new round of infection. ER, endoplasmic reticulum.
Reference:
- Monoclonal antibodies for the prevention of rabies: theory and clinical practice
- Medical Microbiology. 4th edition. Chapter 61Rhabdoviruses: Rabies Virus
- The cell biology of rabies virus: using stealth to reach the brain
- https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/about.htm
Echo Biosystems is committed to delivering high-quality proteins to support your scientific research. We have developed a series of high-quality rabies virus proteins including glycoprotein G, Matrix protein, Nucleoprotein, and Phosphoprotein to meet your research needs.
- Product Name
- Organism
- Tag (Tag info)
- Expression Host (Source)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)Rabies virus (strain PM) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedYeast
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)Rabies virus (strain PM) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedYeast
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein(G),partialRabies virus (strain PM) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedYeast
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein(G),partial
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)Rabies virus (strain PM) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)Rabies virus (strain PM1503/AVO1) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-B2M-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein(G),partialRabies virus (strain HEP-Flury) (RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein(G),partial
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein G(G),partialRabies virus (strain HEP-Flury) (RABV)Tag-FreeE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Glycoprotein G(G),partial
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)Rabies virus(strain SAD B19)(RABV)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)Rabies virus(strain SAD B19)(RABV)N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Nucleoprotein(N)
-
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)Rabies virus (strain CVS-11) (RABV)N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Rabies virus Matrix protein(M)
- rabies virus
